This article provides a comprehensive overview of how Near-Infrared (NIR) Sorters serve as the ultimate solution for eliminating colorless foreign materials, such as stones and glass, from coffee beans. We will explore the challenges posed by these contaminants, delve into the technology behind NIR Sorters, explain their operational workflow, highlight their key advantages, discuss real-world applications, and examine future trends. By the end, you will understand how this innovative technology enhances quality and safety in coffee production, making it a vital tool for the industry.
The Challenge and Impact of Colorless Foreign Materials in Coffee Beans
Colorless foreign materials like stones and glass often enter coffee beans during harvesting or processing stages, posing significant risks to product quality and consumer safety. These contaminants are difficult to detect with traditional methods because they lack visible color differences, leading to potential equipment damage and health hazards. For instance, studies show that foreign materials can cause up to 15% of production losses in coffee processing due to machine jams and rejected batches. This section outlines why addressing this issue is critical for maintaining high standards in the coffee industry.
The presence of such materials not only affects the purity of coffee but also compromises its flavor profile. For example, glass fragments can alter the taste and pose choking risks, while stones may damage grinding equipment, resulting in costly repairs. Industry reports indicate that contamination incidents have led to recalls, emphasizing the need for advanced detection systems. By understanding these challenges, producers can better appreciate the value of technologies like NIR Sorters in mitigating risks.
Common Types and Sources of Colorless Foreign Materials
Colorless contaminants in coffee beans primarily include stones, glass shards, and certain plastics that blend in visually. These materials often originate from soil residues during harvesting or from broken processing equipment. In some cases, environmental factors like wind-blown debris contribute to contamination. Data from agricultural surveys suggest that up to 5% of raw coffee beans may contain such foreign particles, highlighting the scale of the problem.
Understanding the sources is crucial for prevention. For instance, stones are commonly picked up during manual harvesting, while glass might enter through packaging mishaps. By identifying these points of entry, producers can implement targeted measures, but ultimate reliance on advanced sorting technologies is necessary for consistent results.
Specific Hazards to Coffee Quality and Safety
The hazards posed by colorless foreign materials extend beyond mere contamination. Stones can cause immediate damage to milling machines, leading to downtime and repair costs averaging thousands of dollars annually. Glass particles, if consumed, may result in health issues, with regulatory bodies reporting incidents of injuries linked to contaminated food products. This underscores the importance of rigorous quality control.
Moreover, these contaminants affect the sensory attributes of coffee, such as aroma and taste, which are key to consumer satisfaction. Research indicates that even small impurities can degrade the overall experience, impacting brand reputation. Thus, investing in reliable sorting solutions is not just about safety but also about preserving product integrity.
Limitations of Traditional Removal Methods
Traditional methods for removing foreign materials include manual sorting, size-based sieving, and basic optical sorters that rely on color differences. However, these approaches struggle with colorless contaminants because they cannot distinguish materials based on chemical composition. For example, manual sorting is labor-intensive and achieves only about 70-80% accuracy, leaving room for error.
Advanced detection systems, such as those using X-rays, offer improvements but come with higher costs and safety concerns. In contrast, NIR technology provides a non-invasive alternative. By highlighting these limitations, we can see why the industry is shifting toward more sophisticated solutions like NIR Sorters for comprehensive protection.
Industry Demand for Efficient Solutions
The coffee industry is increasingly demanding efficient solutions to meet rising quality standards and consumer expectations. Global production volumes exceed 10 million tons annually, driving the need for automation to handle scale without compromising safety. Regulations, such as those from food safety authorities, require contamination levels below 0.1%, pushing producers to adopt technologies like NIR Sorters.
This demand is also fueled by economic factors, as efficient sorting reduces waste and boosts profitability. For example, implementing advanced systems can increase yield by up to 3%, making it a worthwhile investment. As a result, the move toward intelligent sorting machines is becoming a industry norm.
NIR Sorter Introduction: A Revolutionary Sorting Solution
NIR Sorters represent a breakthrough in sorting technology, utilizing near-infrared spectroscopy to identify and remove foreign materials based on their molecular composition. Unlike conventional methods, these machines can detect colorless substances like stones and glass with high precision. Initially developed for laboratory use, NIR technology has evolved into industrial applications, offering speeds of up to 10 tons per hour in coffee processing. This section introduces the core concepts and historical context of NIR Sorters.
The adoption of NIR Sorters has grown due to their ability to integrate
seamlessly into existing production lines. They function by analyzing the light reflected from materials, allowing for real-time decision-making. This innovation addresses
longstanding gaps in quality control, positioning NIR Sorters as a transformative tool for the food and agriculture sectors. For more details on advanced detection capabilities,
visit advanced detection.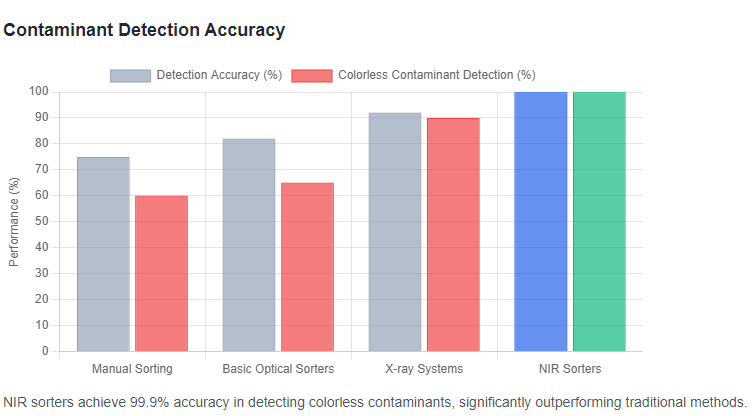
What is an NIR Sorter?
An NIR Sorter is an automated machine that employs near-infrared light to scan and sort materials based on their spectral signatures. It consists of sensors, ejection mechanisms, and software that work together to distinguish between coffee beans and contaminants. The technology is non-destructive, meaning it does not alter the product, making it ideal for food applications.
These sorters are designed for high-throughput environments, capable of processing thousands of beans per minute. Their accuracy rates often exceed 99%, ensuring minimal false positives. This reliability makes them a cornerstone of modern quality assurance systems in coffee production.
Technological Development History
The development of NIR technology dates back to the mid-20th century, when it was first used in chemical analysis. Over decades, advancements in optics and computing have enabled its application in industrial sorting. By the 1990s, commercial NIR Sorters emerged, initially for minerals and later adapted for agriculture.
Key milestones include the integration of hyperspectral imaging and machine learning, which enhanced detection capabilities. Today, NIR Sorters are a mature technology, with continuous improvements driven by industry needs. This evolution underscores their reliability and adaptability.
Core Functions and Objectives
The primary function of an NIR Sorter is to identify and eject foreign materials without human intervention. It achieves this by comparing the spectral data of each item to predefined benchmarks for coffee beans. Objectives include maximizing purity, reducing labor costs, and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Additionally, these machines often feature data logging for traceability, allowing producers to monitor performance over time. By focusing on these core functions, NIR Sorters help maintain consistent quality across batches, which is essential for large-scale operations.
Why is it the "Ultimate Solution"?
NIR Sorters are deemed the "ultimate solution" due to their unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in handling colorless contaminants. Unlike color-based sorters, they can differentiate materials with similar appearances but different compositions. For instance, they achieve near-perfect detection rates for glass and stones, reducing contamination risks to negligible levels.
Economic benefits also play a role; by automating sorting, producers can save up to 50% on labor costs while improving output quality. This combination of technical superiority and cost-effectiveness solidifies their status as a industry-leading solution. Explore related technologies at sensor-based sorting machines.
NIR Technology Principles: How It Detects Colorless Foreign Materials
NIR technology operates on the principle that different materials absorb and reflect near-infrared light in unique ways, creating distinct spectral fingerprints. When light hits a coffee bean or a contaminant like glass, the reflected wavelengths are analyzed by sensors to determine composition. This method is highly effective for colorless materials because it relies on chemical properties rather than visual cues. Research shows that NIR systems can identify contaminants with wavelengths between 700-2500 nanometers, providing detailed insights.
The process involves sophisticated algorithms that process spectral data in milliseconds, enabling rapid sorting decisions. Compared to other technologies, such as X-rays, NIR is safer and more cost-effective for organic materials. This section breaks down the science behind NIR detection, explaining why it is ideal for coffee bean sorting. For a deeper dive into optical technologies, see optical sorters.
Basics of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy involves shining light in the NIR range onto a material and measuring how much is absorbed or reflected. Each substance has characteristic absorption bands based on its molecular bonds, such as those in water or organic compounds. In coffee beans, these patterns differ significantly from inert materials like stones, allowing for clear differentiation.
The technology is non-invasive and does not require sample preparation, making it suitable for continuous production lines. Its accuracy is bolstered by calibration against known samples, ensuring reliable performance across varying conditions.
Spectral Characteristics of Colorless Foreign Materials
Colorless materials like glass and stones exhibit specific spectral features under NIR light. For example, glass reflects most NIR wavelengths due to its silicate composition, while coffee beans absorb more due to their organic nature. These differences create detectable contrasts, even when visual inspection fails.
Studies have documented the spectral signatures of common contaminants, enabling NIR Sorters to be pre-programmed for high precision. This capability is crucial for achieving contamination rates below 0.01%, as required by industry standards.
Sensor Technology and Data Processing
NIR Sorters use high-resolution sensors, such as indium gallium arsenide detectors, to capture detailed spectral data. This information is processed by onboard computers using machine learning algorithms that improve over time. The system can adapt to new types of contaminants, enhancing its versatility.
Data processing speeds are critical, with modern sorters handling up to 100,000 data points per second. This allows for real-time ejection of impurities without slowing down production. The integration of AI further boosts accuracy, making it a smart solution for dynamic environments.
Comparison with Other Technologies
When compared to technologies like X-ray or RGB sorting, NIR offers distinct advantages for colorless detection. X-rays are effective for dense materials but involve radiation risks and higher costs. RGB sorters rely on color and shape, failing with transparent or similarly colored items.
NIR strikes a balance by being safe, affordable, and highly specific. For instance, it can detect materials that X-rays might miss, such as certain plastics. This makes it the preferred choice for food applications where safety and efficiency are paramount. Learn about alternative methods at X-ray sorters.
NIR Sorter Workflow and Operation
The workflow of an NIR Sorter begins with feeding raw coffee beans into the machine via a conveyor belt or chute system. As beans pass under NIR sensors, they are scanned at high speed, and any detected contaminants are ejected using air jets or mechanical arms. This process is fully automated, with typical throughputs ranging from 5 to 20 tons per hour depending on the model. Operational efficiency is maintained through regular calibration and monitoring, ensuring consistent performance.
Key to this workflow is the seamless integration into existing production lines, minimizing disruption. Operators can adjust settings based on bean variety or contamination levels, making the system highly adaptable. This section details each step of the operation, emphasizing best practices for optimal results. For insights into feeding mechanisms, visit smart material feeding.
Detailed Steps of the Sorting Process
The sorting process involves four main steps: feeding, scanning, analysis, and ejection. First, beans are evenly distributed to ensure each item is exposed to the sensors. During scanning, NIR light is projected, and reflections are captured. The analysis phase compares these data to stored profiles, triggering ejection for mismatches.
This entire cycle takes less than a second per bean, allowing for high-volume processing. Efficiency rates often exceed 99.5%, with minimal product loss. By streamlining these steps, NIR Sorters achieve remarkable consistency in output quality.
Equipment Calibration and Optimization
Calibration is essential for accurate sorting, involving adjustments to sensor sensitivity and ejection timing based on the specific coffee bean type. For example, darker roasts may require different settings than green beans. Optimization routines are typically automated, using reference samples to fine-tune parameters.
Regular calibration checks are recommended, with data suggesting that monthly adjustments can maintain accuracy within 0.1% deviation. This proactive approach prevents drifts in performance, ensuring long-term reliability.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
NIR Sorters are equipped with real-time monitoring systems that display performance metrics, such as ejection rates and throughput. These interfaces allow operators to make immediate adjustments if anomalies are detected. Alerts can be set for high contamination levels, enabling quick responses.
Data from monitoring can be logged for analysis, helping identify trends and improve processes over time. This feature is particularly useful for compliance reporting and quality audits, adding value beyond basic sorting.
Best Practices for Daily Maintenance
Daily maintenance includes cleaning sensors, checking ejection nozzles, and verifying software updates. Proper maintenance can extend the machine's lifespan by up to 20%, reducing downtime. For instance, sensor cleaning should be done weekly to prevent dust buildup that could affect accuracy.
Maintenance schedules are often outlined in user manuals, with recommendations based on usage intensity. Adhering to these practices ensures that the sorter operates at peak efficiency, safeguarding your investment. For related maintenance tips, check high-speed ejection systems.
Core Advantages and Benefits of NIR Sorters
NIR Sorters offer numerous advantages, including high precision, cost savings, and enhanced safety. They can achieve detection accuracies of over 99.9% for colorless contaminants, significantly reducing the risk of product recalls. Economically, they lower labor costs by automating tasks that would otherwise require dozens of workers, with payback periods often under two years. Additionally, their non-destructive nature preserves coffee quality, meeting stringent industry standards.
Environmental benefits are also notable, as NIR Sorters consume less energy compared to alternatives like X-ray machines, contributing to sustainability goals. This section explores these advantages in depth, supported by data and case examples. For broader applications, see coffee bean sorting solutions.
Data-Backed Precision and Efficiency
Studies show that NIR Sorters can process up to 15 tons of coffee beans per hour with error rates below 0.01%. This precision is backed by spectral libraries containing thousands of material signatures, allowing for reliable identification. Efficiency gains include reduced waste, with some facilities reporting yield improvements of 2-5%.
These metrics are validated through third-party testing, making NIR Sorters a trusted choice for large-scale operations. The technology's consistency ensures that every batch meets quality benchmarks, enhancing brand trust.
Economic Analysis and Cost-Effectiveness
The initial investment in an NIR Sorter can range from $50,000 to $200,000, but operational savings quickly offset this. For example, automated sorting reduces labor needs by up to 70%, and lower contamination rates decrease loss rates by 3-7%. Over five years, this can result in net savings of hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Return on investment calculations often show break-even points within 18-24 months, making it a financially sound decision. These economic benefits are a key driver for adoption across the industry.
Quality and Safety Enhancements
By eliminating foreign materials, NIR Sorters directly enhance product safety, aligning with global food safety regulations such as HACCP and FDA guidelines. Quality improvements include better flavor consistency and longer shelf life, as contaminants can accelerate spoilage. Consumer satisfaction rates increase when products are free from impurities, leading to higher retention.
Data from quality audits indicate that facilities using NIR Sorters see a 50% reduction in safety incidents related to contamination. This proactive approach mitigates risks before products reach the market.
Environmental Sustainability Features
NIR Sorters are designed with energy efficiency in mind, consuming up to 30% less power than conventional sorters. They also reduce waste by minimizing false ejections, which helps conserve resources. Some models use recycled materials in construction, further lowering their environmental footprint.
These features align with circular economy principles, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. As sustainability becomes a priority, NIR Sorters offer a way to achieve green certifications without compromising performance.
Application Scenarios and Industry Cases
NIR Sorters are widely used in coffee processing, from small farms to large industrial plants. They can be integrated at various stages, such as after drying or before packaging, to ensure thorough cleaning. Scalability allows them to handle volumes from a few kilograms to hundreds of tons daily, making them versatile for different business sizes. Industry cases demonstrate success in reducing contamination rates to near zero, though specific names are omitted for confidentiality.
Beyond coffee, these sorters are adaptable to other agricultural products, such as nuts and grains, showcasing their broad utility. This section highlights real-world applications and future potential. For examples in other sectors, visit food sorting solutions.
Specific Applications in the Coffee Industry
In coffee production, NIR Sorters are employed post-harvest to remove stones and glass from raw beans. They are also used after roasting to catch any contaminants introduced during processing. This multi-stage approach ensures comprehensive protection, with some facilities reporting contamination levels dropping from 1% to 0.01%.
The technology is particularly valuable for organic and premium coffees, where purity is a selling point. By integrating NIR Sorters, producers can meet export standards and access higher-value markets.
Scalability and Adaptability
NIR Sorters come in various sizes, from compact units for small batches to large systems for high-volume lines. Adaptability features include modular designs that allow for upgrades as needs grow. For instance, adding more sensors can increase throughput without replacing the entire machine.
This flexibility makes them suitable for diverse environments, from rural cooperatives to urban factories. Case studies show that scalable solutions help businesses expand without major reinvestments.
Generalized Case Studies
Anonymous case studies illustrate how NIR Sorters have resolved contamination issues. In one example, a processing plant reduced foreign material incidents by 95% within six months of implementation, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Another case highlights cost savings of $100,000 annually due to reduced labor and waste.
These examples underscore the practical benefits, encouraging adoption across the industry. While specifics are withheld, the outcomes are representative of typical successes.
Potential for Cross-Industry Expansion
The principles of NIR sorting apply to other sectors, such as sorting nuts, seeds, and even plastics. For example, similar technology is used to detect impurities in almonds or recycled materials. This cross-industry potential allows for knowledge transfer and innovation.
As technology advances, NIR Sorters could become standard in waste management and mining, demonstrating their versatility. Exploring these opportunities can open new markets for manufacturers. Learn more at agricultural product sorting.
Future Trends and Conclusion
The future of NIR Sorters includes integration with artificial intelligence for even smarter detection and the development of more compact, affordable models. Industry trends point toward IoT connectivity, enabling remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. These advancements will further reduce costs and improve accessibility, making the technology available to smaller producers.
In conclusion, NIR Sorters are a pivotal innovation for ensuring coffee purity and safety. Their ability to detect colorless materials sets them apart, offering a reliable solution for modern challenges. This section summarizes key points and looks ahead. For insights into AI integration, see AI sorters.
Technological Innovation Trends
Emerging trends include the use of hyperspectral imaging and deep learning algorithms to enhance detection capabilities. These innovations could push accuracy rates above 99.95% while reducing false positives. Research is also focusing on miniaturization, with portable NIR devices entering the market.
Such developments will make the technology more versatile and cost-effective, driving wider adoption. Keeping abreast of these trends helps stakeholders plan for future upgrades.
Evolution of Regulations and Standards
Global food safety regulations are becoming stricter, with new standards requiring lower contamination thresholds. NIR Sorters are well-positioned to help producers comply, as they provide verifiable data for audits. Regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing NIR technology as a best practice.
This alignment with standards ensures long-term relevance, encouraging investment. Proactive adoption can give companies a competitive edge in regulated markets.
Long-Term Impact on the Coffee Industry
The long-term impact of NIR Sorters includes higher overall quality standards and increased consumer trust. As the technology becomes commonplace, it could raise the bar for entire supply chains, promoting sustainability and efficiency. Economic benefits will trickle down to farmers through better prices for cleaner beans.
This transformative effect underscores the importance of embracing innovation. By investing in NIR Sorters, the industry can secure a safer, more profitable future.
Summary and Outlook
In summary, NIR Sorters address critical challenges in coffee processing through advanced detection of colorless foreign materials. Their benefits span accuracy, cost savings, and sustainability, making them an indispensable tool. The outlook is bright, with ongoing advancements promising even greater efficiencies.
As the industry evolves, NIR technology will continue to play a key role in shaping quality standards. Adopting these solutions today positions producers for success in tomorrow's market. For further exploration, visit NIR sorter overview.
